I don't profess to be an expert on pigments, I don't even try to remember them but have a vague knowledge of the main ones I use and look them up as needed. It is important to understand a few basics regarding paint properties and to keep the number of paints to a manageable quantity, particularly when learning. I used a fairly limited palette of W & N artist quality paints for well over 20 years before adding any extras and they are one of the better brands and consistent. I don't think having more paints made my painting any better. Sometimes the fancy names and marketing by companies like Daniel Smith and Sennelier make paints seem very attractive and you can end up with far too many, more often than not the 'convenience' mixes are completely unnecessary but they can be fun to play with. I learned from mistakes, by experimenting and reading. If you want to find out about paints I recommend Hilary Page's Guide to Watercolour paints, which is probably one of the most comprehensive tests of different brands, she updates online too. And the excellent Handprint website provides everything you could ever need to know!
I'm afraid I don't paint beautiful elaborate colour charts, painting pages of squares with no particular purpose seems quite pointless to me as the number of variations is infinite but again when learning it can be useful to experiment with colour mixes in this way. Instead I tend to paint colour charts on a 'needs' basis when working on a subject.
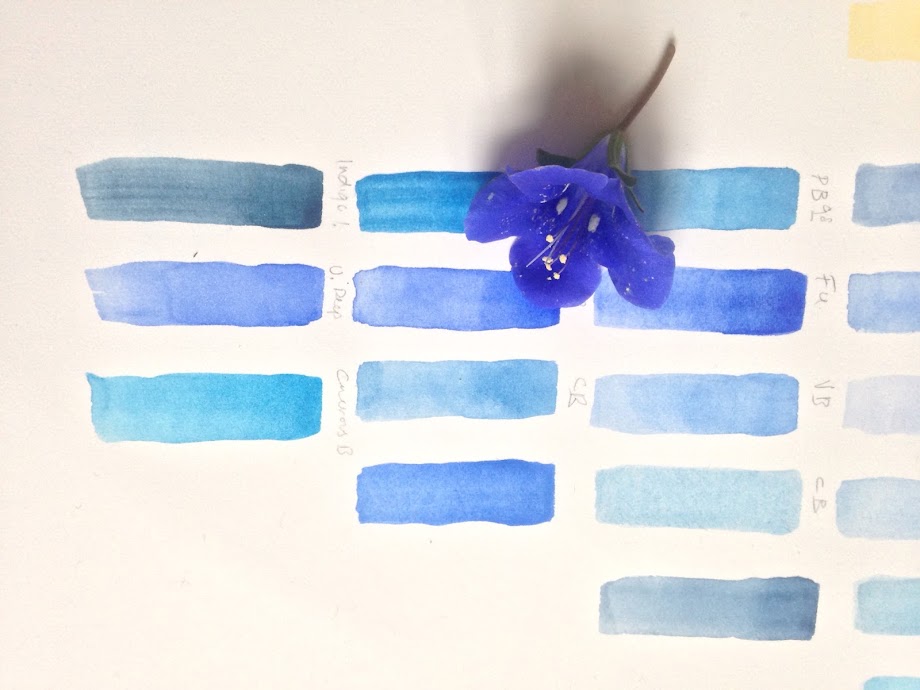
How I mix colours
I'm not saying this is right or wrong - it's just my way. To match a primary, such as this blue flower below, first of all I refer to a painted chart of all the paints I have of the same hue, I hold the subject next to the samples in good daylight to identify the nearest match. I try to match to the nearest basic hue first. From there I look for the cool and warm variations in relation to light and make a colour chart. After the hue has been identified I consider the saturation of the colour and the tonal values. It's very important to understand these 3 key points. It's surprising how often saturation is confused with tone. I won't go into it here or this post will never end. I think it was covered it in a previous post.
 |
| Orange can be a tricky secondary colour mixed using yellow and red pigments, although Daniel Smiths Transparent Pyroll Orange is a nice single pigment orange too for glazes |
 |
| My not very tidy colour charts for the Fritillaria imperialis painting |
This next section is about the basic properties. Followed by a comparison of brands on an actual subject.
Some of the things nobody ever told me....a beginners guide
I can recall having no idea what anybody was talking about when it came to paint properties and feeling a bit foolish, but how was I to know if nobody ever taught me! When I started to learn I realised that I has already discovered many of the the attributes of paints through using them on a regular basis but just didn't know the terminology.
I purchased my first watercolour box, 36 years ago when I was 15. It had 12 pans of fairly standard colours, you can still buy a similar box today from W & N although the cadmiums are no longer included. The only thing I knew was that my art teacher had told me to buy the artist quality paints. I wasn't taught anything about paint properties at school or art school or on any . There was no Internet, so I went to my local art store, which is still in business today and purchased the only box of paints in stock using some money I'd saved from my birthday. Here are a few of the basic points that might be useful.
Paint properties
Each tube or pan of paint in your paintbox has a different properties listed, pigments, lightfast or ASTM ratings, transparency or opacity, staining properties etc. are all listed on the tube or on a colour chart.
Thirty five years ago, I just used my
paints.....a lot..... and it's the best way to learn. I was pretty happy with them but became slightly frustrated by a 'flatness' that was evident
in some mixes and couldn't quite achieve the vibrant colours found in
nature when I layered washes.I wanted to know more. I started to buy
odd few bright colours and moved up a size with the paint box to the 24
pans, which I used for around 20 years before moving on to the wooden box of pans that I still use
today. Then I started to add but many colours I hardly ever use. Most important to me was transparency, all watercolours are transparent to some degree but some are more transparent
than others. I also noticed the effect of granulation in certain
colours. I also realised that
some colours can fade or stain and that they can be made of single or
multiple pigments. I started to read and learn more.
The easiest way to find out about paint properties is to download or send off for a colour chart, many are free from companies such as Jacksons Art.
There are some links at the end of this blog post to download charts. Download the chart and simply paint your own version and write on the properties and observational notes. Keep it in your paintbox or on your drawing board for reference ( One of mine is shown in the image below).
Types of pigment
Watercolour paints are made of pigment and an aqueous medium which suspends that pigment, with binder, such as gum Arabic (which can crack if there is too much) and a plasticizer, such as honey.
As a simple explanation, there are broadly two types of pigments
1. Inorganic or mineral, which are derived from the earth's minerals and include many opaque colours, these include the natural earth colours such as the ochres and siennas or the synthetic mostly metallic elements such as the cobalts and cadmiums
2. Organic pigments which are created in a laboratory, are derived from either natural animal or plant matter or from synthetic oil based chemicals include many of the bright transparent colours, such as the quinocridones pthalo, dioxazine and hansa colours. They are very useful to the botanical artist because they allow us to create the bright colours found in nature.
Before the Industrial revolution and the development of synthetic pigments the artist had a much more limited palette. Pigments were hard to extract an prices of certain pigments were prohibitive. Today, with synthetic pigments we have a huge range of paints at our disposal. Manufacturers apply all sorts of exotic names to their colours, which tends to attract our attention.
If you look at colour charts or paint tubes or pans you will see that each paint has a brand name, this can be quite misleading and often the name doesn't relate to the pigment. Paints can have the same name but different pigments e.g. Daniel Smith Indian Yellow is PY 108 and W & N is PY 153. So if you try to but the same colour name in a different brand check the pigment number first. You will also find an an alpha numeric code that starts with P ( Pigment ) then a letter for the pigment followed by a number, e.g. PV 14 and PV 49 are both Cobalt Violet but PV14 is Cobalt Phosphate and PV 49 is a newer pigment which also contains ammonium. Cobalt violet is a favourite of mine I use it a lot for reflected light and seem to have it from several manufacturers! Using single pigments paints is probably the most reliable route for reasons I've already mentioned but even with the same pigment brands do differ considerably as shown below.
Student versus Artist Quality
Artist quality paints are generally superior to student quality because they have higher pigment to mixer ratios, and therefore the tinting quality is superior. The pigment may also be less finely ground or poorer quality with more fillers. If you compare the two you will see that the student quality have a slightly chalky and less translucent appearance. It's worth buying less paints of a better quality.
Pans or Tubes
As a rule of thumb pans are suited to smaller works, painted used a 'dryer' style, whereas tubes which are already suspended in liquid are meant to be used wet. Some tubes, such as M. Graham are suitable for re-wetting.
As a rule of thumb if you like painting wet-in wet and big washes, use tubes but if you prefer fine detail on a smaller scale pans are better. I use a mix of both although I used pans for many years and still prefer them for painting on vellum. I wouldn't recommend buying the full pans unless you are certain it's a s colour you will use a lot.
Pans have a higher pigment ratio and are easy to store and transport, The downside is that they get dirty and fluffy if you forget to close the paintbox lid! Tubes are good for getting larger amounts of colour onto the palette and a higher paint load on the brush which is advantage when working on larger washes. Don't allow them to dry and reuse unless they are suited to such treatment, some brand degrade when dried. My frustration with tubes is the lids, which never seem to want to go on or weld on so tight that it's almost impossible to get them off. Again neither tubes or pans are better they are just different and you can probably find a use for both.
Lightfastness
The ASTM ( American Society for Testing and Materials) is the recognised testing system to assess the lightfasness in paint over time under the effect of light. This system became more stringent in 1983 and as a result manufacturers appear more conscientious regarding the longevity and stability of paints. Paints are rated I (excellent) or II ( very good) are tested and known to be reliable. Some florilegiums and societies ask that artists use only paints with these ratings, and if you are selling your work you have a responsibility as an artist to ensure that the work is a permanent as possible. The paints rated III ( moderate) and IV (poor) should therefore be avoided. A designation of N/A means the paint has not been rated. There are several that should be avoided, such as the fugitive Opera, and rose madder genuine, Alizarin Crimson. There are also ratings for fluctuating colour, reaction to acidity / alkalinity and damp. Aureolin is known to which becomes dirty in thin washes.Check the ratings on the colour chart. You can carry out your own lightfast tests too.
The Watercolour purist method and white paint
This is the method that I use, it basically means that the white of the paper is used instead of adding any white paint, it relies on the transparency of the paints so the paints used need to be carefully considered to ensure that luminosity is retained. An occasion some white body colour, such as titanium or Chinese white may be added, such as on the white hairs of a flower or leaf or bloom on a fruit. This is applied last of all and applied fairly dry with a small fine brush. Other than this use white should be avoided.
Paints with Black
Another reason for single pigment paints is the deadening effect of paints with black. Indigo being a case in point. It may look like a beautiful dark rich blue but when used in a green mix it can kill it stone dead. An example is Daniel Smiths Indigo which is PB60 and PBk6 - its a mix of Indanthrone blue and black.
Transparency and opacity
Transparency is particularly important, so something you really should always check, transparency varies between brands too, e.g. PR 179 Daniel Smith Perylene Maroon is semi transparent and
Winsor & Newton is transparent. As I've already mentioned all watercolours are transparent but some more so than others, so glazing with the transparent gives cleaner result than glazing with opaques or semi-opaques. Sounds obvious but you be surprised how many people are puzzled by the the lack of transparency in there painting yet haven't considered the transparency properties. Generally speaking you need a mix of opaque and transparent in your paint box, although like many botanical artists I prefer more transparent paints, the opaques have their place too and can be good for the first washes to lay a foundations. Thereafter the transparent colours are good for subsequent glazing and allow the light to pass through and preserve the luminosity. Try painting a strips of opaque colour then overlay a transparent colour, and vice versa to see the difference.
Granulating colours
Some pigments separate from the water and result in a granulated effect, many occur in the blues,, such as French Ultramarine and Cerulean. This can be a desirable feature but may also be an effect that you don't want. The degree of granulation seems to differ between manufacturers
Staining Pigments
Paint properties
Each tube or pan of paint in your paintbox has a different properties listed, pigments, lightfast or ASTM ratings, transparency or opacity, staining properties etc. are all listed on the tube or on a colour chart.
 |
| Tube of paint showing properties. |
The easiest way to find out about paint properties is to download or send off for a colour chart, many are free from companies such as Jacksons Art.
There are some links at the end of this blog post to download charts. Download the chart and simply paint your own version and write on the properties and observational notes. Keep it in your paintbox or on your drawing board for reference ( One of mine is shown in the image below).
 |
| Keep a painted chart in the lid of your paintbox and another on your drawing board, which shows the full strength and in glazes. |
Watercolour paints are made of pigment and an aqueous medium which suspends that pigment, with binder, such as gum Arabic (which can crack if there is too much) and a plasticizer, such as honey.
As a simple explanation, there are broadly two types of pigments
1. Inorganic or mineral, which are derived from the earth's minerals and include many opaque colours, these include the natural earth colours such as the ochres and siennas or the synthetic mostly metallic elements such as the cobalts and cadmiums
2. Organic pigments which are created in a laboratory, are derived from either natural animal or plant matter or from synthetic oil based chemicals include many of the bright transparent colours, such as the quinocridones pthalo, dioxazine and hansa colours. They are very useful to the botanical artist because they allow us to create the bright colours found in nature.
 |
| Natural Ultramarine Pigment derived from the mineral Lapis Lazuli copyright Wikimedia Commons |
Before the Industrial revolution and the development of synthetic pigments the artist had a much more limited palette. Pigments were hard to extract an prices of certain pigments were prohibitive. Today, with synthetic pigments we have a huge range of paints at our disposal. Manufacturers apply all sorts of exotic names to their colours, which tends to attract our attention.
If you look at colour charts or paint tubes or pans you will see that each paint has a brand name, this can be quite misleading and often the name doesn't relate to the pigment. Paints can have the same name but different pigments e.g. Daniel Smith Indian Yellow is PY 108 and W & N is PY 153. So if you try to but the same colour name in a different brand check the pigment number first. You will also find an an alpha numeric code that starts with P ( Pigment ) then a letter for the pigment followed by a number, e.g. PV 14 and PV 49 are both Cobalt Violet but PV14 is Cobalt Phosphate and PV 49 is a newer pigment which also contains ammonium. Cobalt violet is a favourite of mine I use it a lot for reflected light and seem to have it from several manufacturers! Using single pigments paints is probably the most reliable route for reasons I've already mentioned but even with the same pigment brands do differ considerably as shown below.
Student versus Artist Quality
Artist quality paints are generally superior to student quality because they have higher pigment to mixer ratios, and therefore the tinting quality is superior. The pigment may also be less finely ground or poorer quality with more fillers. If you compare the two you will see that the student quality have a slightly chalky and less translucent appearance. It's worth buying less paints of a better quality.
Pans or Tubes
As a rule of thumb pans are suited to smaller works, painted used a 'dryer' style, whereas tubes which are already suspended in liquid are meant to be used wet. Some tubes, such as M. Graham are suitable for re-wetting.
As a rule of thumb if you like painting wet-in wet and big washes, use tubes but if you prefer fine detail on a smaller scale pans are better. I use a mix of both although I used pans for many years and still prefer them for painting on vellum. I wouldn't recommend buying the full pans unless you are certain it's a s colour you will use a lot.
Pans have a higher pigment ratio and are easy to store and transport, The downside is that they get dirty and fluffy if you forget to close the paintbox lid! Tubes are good for getting larger amounts of colour onto the palette and a higher paint load on the brush which is advantage when working on larger washes. Don't allow them to dry and reuse unless they are suited to such treatment, some brand degrade when dried. My frustration with tubes is the lids, which never seem to want to go on or weld on so tight that it's almost impossible to get them off. Again neither tubes or pans are better they are just different and you can probably find a use for both.
Lightfastness
The ASTM ( American Society for Testing and Materials) is the recognised testing system to assess the lightfasness in paint over time under the effect of light. This system became more stringent in 1983 and as a result manufacturers appear more conscientious regarding the longevity and stability of paints. Paints are rated I (excellent) or II ( very good) are tested and known to be reliable. Some florilegiums and societies ask that artists use only paints with these ratings, and if you are selling your work you have a responsibility as an artist to ensure that the work is a permanent as possible. The paints rated III ( moderate) and IV (poor) should therefore be avoided. A designation of N/A means the paint has not been rated. There are several that should be avoided, such as the fugitive Opera, and rose madder genuine, Alizarin Crimson. There are also ratings for fluctuating colour, reaction to acidity / alkalinity and damp. Aureolin is known to which becomes dirty in thin washes.Check the ratings on the colour chart. You can carry out your own lightfast tests too.
The Watercolour purist method and white paint
This is the method that I use, it basically means that the white of the paper is used instead of adding any white paint, it relies on the transparency of the paints so the paints used need to be carefully considered to ensure that luminosity is retained. An occasion some white body colour, such as titanium or Chinese white may be added, such as on the white hairs of a flower or leaf or bloom on a fruit. This is applied last of all and applied fairly dry with a small fine brush. Other than this use white should be avoided.
Another reason for single pigment paints is the deadening effect of paints with black. Indigo being a case in point. It may look like a beautiful dark rich blue but when used in a green mix it can kill it stone dead. An example is Daniel Smiths Indigo which is PB60 and PBk6 - its a mix of Indanthrone blue and black.
Transparency and opacity
Transparency is particularly important, so something you really should always check, transparency varies between brands too, e.g. PR 179 Daniel Smith Perylene Maroon is semi transparent and
Winsor & Newton is transparent. As I've already mentioned all watercolours are transparent but some more so than others, so glazing with the transparent gives cleaner result than glazing with opaques or semi-opaques. Sounds obvious but you be surprised how many people are puzzled by the the lack of transparency in there painting yet haven't considered the transparency properties. Generally speaking you need a mix of opaque and transparent in your paint box, although like many botanical artists I prefer more transparent paints, the opaques have their place too and can be good for the first washes to lay a foundations. Thereafter the transparent colours are good for subsequent glazing and allow the light to pass through and preserve the luminosity. Try painting a strips of opaque colour then overlay a transparent colour, and vice versa to see the difference.
Granulating colours
Some pigments separate from the water and result in a granulated effect, many occur in the blues,, such as French Ultramarine and Cerulean. This can be a desirable feature but may also be an effect that you don't want. The degree of granulation seems to differ between manufacturers
Staining Pigments
Once you put them on the paper they're there to stay and hard to lift. Examples include the cadmium reds and yellows.
Paints with Hue in their name
Paints with Hue in the name tend to be an imitation of another pigment. For example Manganese Blue Hue. Manganese Blue is no longer available so the Hue is a combination of Pigments to match the original pigment. Many of the Hue paints replace toxic pigments.
Is one brand preferable to another? A simple test painting the same subject
I don't think so, although some seem to be more consistent. I tried painting the same small subject using the same pigments ( or as near as possible). I used Daniel Smith, Schmincke, W & N and M. Graham. I decided not to bother with Sennelier as I couldn't match the pigments and don't care for them anyway.
Paints with Hue in their name
Paints with Hue in the name tend to be an imitation of another pigment. For example Manganese Blue Hue. Manganese Blue is no longer available so the Hue is a combination of Pigments to match the original pigment. Many of the Hue paints replace toxic pigments.
Is one brand preferable to another? A simple test painting the same subject
I don't think so, although some seem to be more consistent. I tried painting the same small subject using the same pigments ( or as near as possible). I used Daniel Smith, Schmincke, W & N and M. Graham. I decided not to bother with Sennelier as I couldn't match the pigments and don't care for them anyway.
 |
| Red Maple seeds completed using the same pigments but different brands, top: Daniel Smith and Schmincke ( pans), bottom: Winsor & Newton (pans) and M. Graham |
Overall I found it made very little difference. I'm happy to work with any of these paints, they are all of very good quality and find I prefer some colours in one brand but don't like it in another. I think as long as you have a good artist quality set of single pigment paints you can make a decent enough painting. Personal preference and technique will influence your choice.
The Palette
There is no perfect palette but as a basic start I think two of each primary ( one warm and one cool) plus one other and a few brights will do the job! If you're a beginner. Learn about those first and try others later when you understand the properties. Here are some of my favourites.
BLUES: French Ultramarine PB29, Cobalt Blue PB28, Cerulean blue PB35 plus Phthalo Blue PB15, Indanthrene blue PB 60,
REDS: Pyrrol Scarlet PR255, Permanent Rose PV19, Permanent Alizarin Crimson PR206 and Quin Red PR209, Quin Magenta PR122 Permanent Magenta PV19
Note: I still like W & N Scarlet lake PR 188 too. It's more lightfast than other and not like the less permanent old paints.
YELLOWS: Nickel Titanium yellow PY53, Winsor Lemon PY175, Winsor Yellow P154, Transparent Yellow PY97, Indian Yellow PY153
You can make most stuff from these but I add a few earths too:
EARTHS:Brown Madder PB 206, Burnt Umber PBr 7 ( M Graham) Burnt Sienna PR 101 and Quin Gold PO 49
EARTHS:Brown Madder PB 206, Burnt Umber PBr 7 ( M Graham) Burnt Sienna PR 101 and Quin Gold PO 49
VIOLETS:Ultramarine violet PV15, Winsor Violet ( Dioxazine) PV23 and Cobalt
violet PV 14 I like these for shadows and reflected light
That's a 'brief' overview, without getting too technical
That's a 'brief' overview, without getting too technical
Colour Charts for the brands discussed:
Buy hand painted W &N chart
Free Chart order from Jacksons Art
You can also buy dot charts from Daniel Smith to try out the paints before buying
Find out more about colour
Books
Books
Ittens, Johannes., Elements of Colour or if you can afford or order from the library The Art of Colour
Albers, Joseph. Interactions of Colour
About Watercolour Paint Books
Page, Hilary. Guide to Watercolour Paint
Websites




























Brilliant post Dianne. A great help to beginners and experienced painters alike. It's a pity more focus is not placed on pigment properties to begin with - would certainly save a lot of grief in the long run. Of course the best way to learn is to practise yourself with the colours and observe their properties, but a little theory goes a long way. All colours are not created equal! If we all knew this from the outset a lot of time would be saved to have the knowledge to check the colour and its properties first before choosing it for that all important painting. Thank you for sharing your vast knowledge and experience.
ReplyDeleteThanks Vicki, absolutely true that practise and self discovery is the way to learn but also agree that a little help and reassurance along the way eases the journey.
DeleteI enjoy all your posts, and this one did not disappoint. Thank you for all the useful information.
ReplyDeleteThank you Carmelle. Hope you found it useful.... It's hard to know how much info is enough sometimes, so really pleased you enjoyed it :)
DeleteFantastic post Dianne and brilliant info for anyone getting to grips with colour mixing and pigments. Thank you for sharing your knowledge x
ReplyDeleteThanks Jarnie, it's bonkers really, I tried to discuss it with the daughter but she fell asleep so I wrote it down instead.... the ramblings of a geek me thinks ;)
DeleteIf there is something every water colour "artist" should now and read, it's this post!!!
ReplyDeleteThank you so much for sharing all your knowledge about it!
I've just started making colour charts, learning what I need to learn with using water colors.
Great, very great help!
Wishing you a nice and creative day!
XX Maria
Thank you Maria, I'm so pleased you found it useful. Have fun with your colour charts x
DeleteIt is worth the long read ! There is so much to tell, to learn and to find out about colours, paints and pigments. It never stops. I understand why it took a while before you finally felt brave enough to write it. Because when you do you need to do it well. And you did... of course! I'm going to share it and keep it in my own files, like some previous posts you wrote. Some day you'll write a book and I'll be the first to buy it ;)
ReplyDeleteThanks Sigrid, I'm way too disorganised to write a book!.... but maybe one day when I'm an old girl and can no longer paint ;)
DeleteThanks Dianne for sharing your knowledge. I enjoy and learn from all of your posts. You have also inspired me to buy a sketchbook now to complete the first white page.
ReplyDeleteVery useful post Dianne - and now in the section about watercolour tips on my website
ReplyDeleteThank you Katherine
DeleteThank you for sharing so much information with all of us!!! I have been painting for many years but learned so much today from one article. I am diving in to learning more so I'll know which pigments I should toss/ or just save for display in the studio!
ReplyDeleteGreat article! We are linking to this great article on our site. Keep up the good writing.
ReplyDeleteProkr.com
3idat.com/jeddah
3kary.com
I wish to say thank you for sharing your knowledge, time and effort. I discovered your site through your silverpoint drawing of a bulb and found your work eye catching and inspiring. One day I will follow one of your tutorials but for the moment I have been focussing on landscape watercolours trying to fathom out how some of the old masters like Girtin and Turner painted monastic buildings with such delicacy and recently discovered some of Rowland Hilder's watercolour colours were helpful, and now having read your article on transparency in watercolours this now completes my research. Thank you once again and good wishes to you for the future.
ReplyDeleteJo Jessop
I never comment but felt like i need to because i keep coming back to ur blog few times a year and especially to this post!
ReplyDeleteI forget about it sometimes and google something about watercolour and i see this post again and click and re-read it.
You are the only person so far that didn't rave about schimncke and daniel smith! everyone else prefers them on other brands and talk much about how good they are and how much better brighter and richer they are than W&N. I'm a beginner but i like to research and look at stuff to build my knowledge and to help me decide what supplies am gonna buy next. I can tell you that you are the only who says that W&N is so good; everyone else says that DS, MG, and Schmincke are way better!
After all the things i've seen online i felt like what they r saying isn't very true as i see a lot of W&N colours looking very bright and rich and not dull and pale which made come back here and appreciate this post even more!
THANK YOU for the honest opinions and informative post.
i just wish you would compare the similar pigments you have of these brands so we could see the vibrancy and transparency better.
I also wish you had included swatches of the colours you recommended for a palette.
Thank you very much again, you helped me a lot.
(I was looking for a picture or video comparing the same colours of these brands all together to see how vibrant they are and didn't find any except yours; it usually only 2 of these not all 4).
Actually many of the people who are fans of Daniel Smith brand, M Graham or Schmincke are masters who have painted for well over 35 to 40 years and actually started out using Winser & Newton. One tube of W&N artist grade sells in China for only one dollar because that's where its made now. Not England or France. Yet the price for us is pretty high for a 14 ml tube. The other brands are 15ml tubes. I know a professional water colorist who dumped Daniel smith for Holbein. its just a matter of preference I guess. LOL
DeleteHey there! This is my first visit to your blog! We are a group of volunteers and starting a new initiative in a community in the same niche. Your blog provided us beneficial information to work on. You have done a outstanding job! hot pink paint
ReplyDeleteAn fascinating discussion is value comment. I think that it is best to write extra on this matter, it won’t be a taboo topic however generally people are not enough to talk on such topics. To the next. Cheers industrial paint
ReplyDeleteI was wondering how long ago it was that you tried Sennelier brand watercolor? Because in 2012 they totally revamped the formula with the new line called Sennelier’s French Artists’ Watercolors – new formula. During this time, art stores were selling the old line at discount prices to get rid of it. Everyone who has tried the new formula are raving about the transparency and luminosity. No chalkiness anymore.
ReplyDeleteI've only just stumbled across this and I know it is an old post, but I completely agree with these paint choices and I also have preferences mostly among these brands too. I'm wondering whether the difficulty with painting with the MG paints on vellum was due to the honey in the binder, noting that it's best to use paint quite dry on vellum.
ReplyDeleteThe one colour I have struggled with is Ultramarine/French Ultramarine PB29 and searching for the least granulating one. My teacher Deirdre Bean found the Holbein French Ultramine Light PB29 to so far be the least granulating, which is best for botanical work.
Unfortunately, I think my paint collection resembles yours. And great that you mentioned the Handprint website. I always consulted it during my paint buying forays!